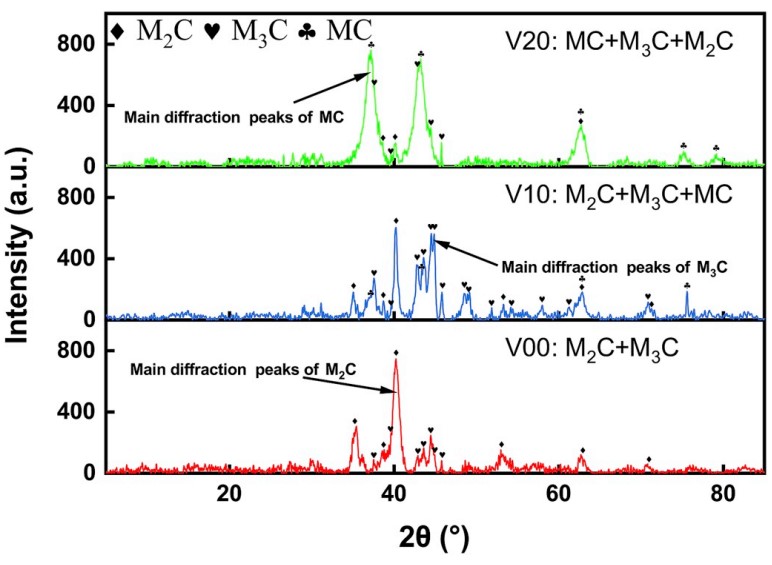
去掉背景具有不同 V 含量的焊缝金属的代表性残留物XRD结果如图所示。很明显,随着 V 含量的增加,试样中的碳化物类型逐渐变化。在没有任何 V 的样品中检测到 M2C(M = Mo,主要)和 M3C(M = Fe,主要)碳化物,而密排六方 M2C 和正交 M3C 的衍射峰很容易辨别。面心立方 MC 的弱衍射峰(M = V,主要)表明少量 MC 碳化物开始在 V10 试样上析出。然而,随着 V 含量增加到 0.18 wt%,M2C 和 M3C 的衍射峰变得非常弱且难以检测,表明大量 M3C 和 M2C 碳化物被相当部分的 MC 碳化物取代。此外,值得注意的是,V00 焊缝金属的 M2C 衍射峰的积分强度明显强于 M3C 峰,但这种强度差异在 V10 焊缝金属中有所降低,表明 M2C 体积分数由于Mo 取代了 MC 碳化物中的 V,而不是形成 M2C。一般来说,碳化物衍射峰积分强度的变化表明 MC 体积分数的增加是由于在 V 存在下 M2C 和 M3C 的牺牲造成的。这些结果表明 0.18 wt% V 稳定在抑制 M3C 和 M2C 析出的必要 C 条件下,更多的热力学 MC 碳化物,因为与 Fe、Mo 和 Cr 相比,V 是最强的碳化物形成元素,这导致Mo 含量高达 0.7 wt% 时,VC比 M3C 和 M2C 具有更大的热力学优势。
The background subtracted XRD patterns of the representative residues of the weld metals with different V contents are depicted in Fig. It is obvious that the carbide types within the specimens gradually changed with an increase in the V contents. M2C (M = Mo, mainly) and M3C (M = Fe, mainly) carbides were detected in the specimen without any V, while reflection peaks for the hexagonal close-packed M2C and orthorhombic M3C were easily discernible. The weak reflection peaks of the face-centred cubic MC (M = V, mainly) indicated that a small amount of MC carbides began to precipitate at the V10 specimen. However, as the V content increased to 0.18 wt%, the reflection peaks of the M2C and M3C became very weak and difficult to detect, suggesting that a large number of M3C and M2C carbides were replaced with a considerable portion of MC carbide. Moreover, it is notable that the integrated intensity of the M2C reflection peaks for the V00 weld metal was obviously stronger than that of the M3C peaks, but this intensity difference was alleviated in the V10 weld metal, indicating a decreasing M2C volume fraction owing to the Mo substituting the V in the MC carbides, instead of forming M2C. In general, the variations in the integrated intensity of the carbide reflection peaks indicated that the an increasing volume fraction of the MC was caused by the sacrifice of the M2C and M3C in the presence of V. These results revealed that the 0.18 wt% V stabilised the more thermodynamic MC carbides under the condition of the requisite C to suppress the M3C and M2C precipitation, because V was the strongest carbide forming element compared to Fe, Mo, and Cr, which resulted in a substantially greater thermodynamic advantage over the M3C and M2C precipitation with Mo contents up to 0.7 wt%.