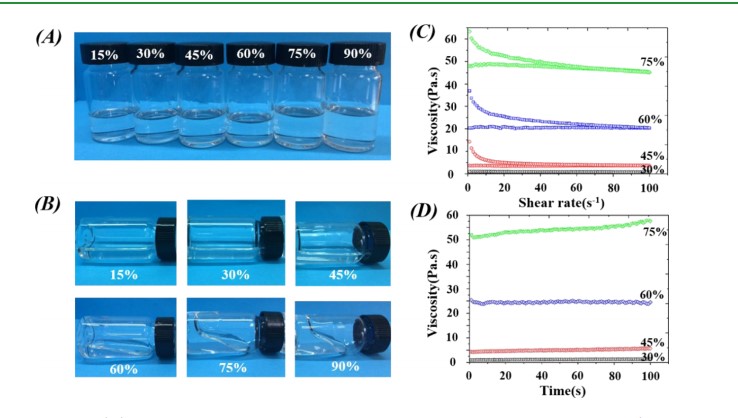
以P-PUU1.2为例,探讨了P-PUU油墨的可打印性与浓度之间的关系。制备了梯度浓度分别为15、30、45、60、75和90%的P-PUU1.2油墨,如图A所示,所有制备的样品均为透明的,没有聚合物残留,表明P-PUU在1,4-二恶烷中具有良好的溶解度。当这些样品水平放置时,我们可以直接观察到P-PUUs的粘度随着浓度的提高而急剧增强,特别是在浓度达到75%之后(图B)。为了获得最适合3D打印的P-PUUs浓度,我们进一步检测了30、45、60和75%P-PUU1.2油墨的流变行为。图C,D的结果表明,60%的P-PUU1.2油墨对空气驱动的挤压3D打印具有适当的粘度,通过3D打印的实际测试进一步证实了这一点。
The P-PUU1.2 was used as an example to explore the relationship between the printability and the concentration of P-PUU inks. P-PUU1.2 inks with a gradient concentration of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90% were prepared as shown in A, and all the as-prepared samples were transparent with no polymer residue, suggesting the excellent solubility of P-PUU in 1,4-dioxane. When placing these samples horizontally, we could directly observe that the viscosity of P-PUUs sharply enhanced with raising concentration, especially after the concentration reached 75% (B). To obtain the most suitable concentration of P-PUUs for 3D printing, the rheological behaviors of 30, 45, 60, and 75% P-PUU1.2 inks were further detected. The results in C,D suggested that 60% P-PUU1.2 ink has appropriate viscosity for the air-driven extrusion 3D printing, which was further confifirmed by the practical test of 3D printing.