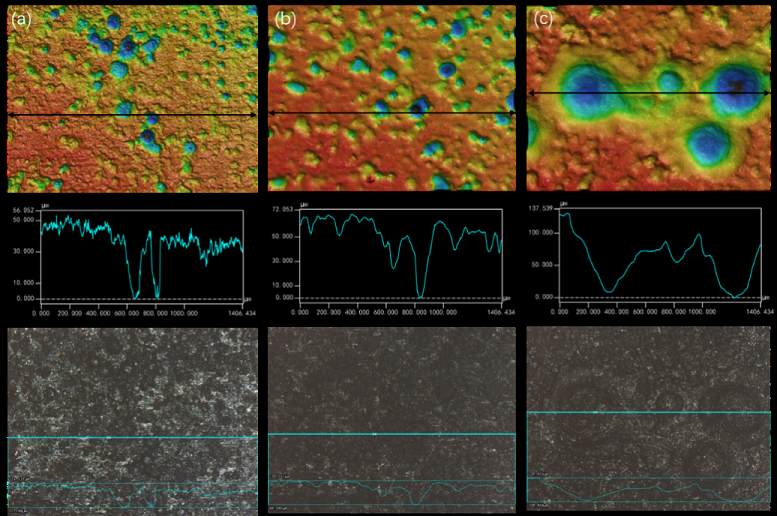
金属焊接-图5-碳钢DH36在达叻现场腐蚀1年后的表面轮廓(a)母材,(b)热影响区,(c)焊缝。通过CO2气体保护焊(250A, 29V, 300mm/min, 14.5 kJ/cm)。
典型钢DH36焊接接头母材、熔合线和焊缝区均受到不同程度的腐蚀,表面布满了大大小小的点蚀坑,从母材区到焊缝区点蚀坑逐渐变大变深,焊缝位置点蚀坑最大半径甚至达到580μm,最大深度130μm;而母材区点蚀坑最大半径只有200μm,深度48μm。说明在热带海洋大气环境下典型钢DH36焊接接头焊缝区受到更加严重的破坏,这主要与焊接过程中焊接接头所经历的热循环过程有关。2年现场腐蚀后表面形貌图表面各区分布了密密麻麻的蚀坑,其中母材的蚀坑数量较多,而热影响区蚀坑表现出大而深的形貌,说明热影响区腐蚀更为严重。
Metal welding - Figure 5 - surface profile of carbon steel DH36 after 1 year of corrosion at Dalat site (a) base metal, (b) heat affected zone, (c) weld. Through CO2 gas shielded welding (250A, 29V, 300mm / min, 14.5 kJ / cm).
Typical steel DH36 welding joint base metal, fusion line and weld area are subject to different degrees of corrosion, the surface is full of large and small pitting pits, from the base metal area to the weld area pitting pits gradually become larger and deeper, the maximum radius of the weld position pitting pit even reaches 580 μ m. Maximum depth 130 μ m; However, the maximum radius of pitting pit in base metal area is only 200 μ m. Depth 48 μ m。 It shows that the weld zone of typical steel DH36 welded joint is more seriously damaged in tropical marine atmosphere, which is mainly related to the thermal cycle process of the welded joint. After two years of in-situ corrosion, dense pits were distributed in each area of the surface, in which the number of pits in the base metal was more, while the pits in the heat affected zone showed a large and deep morphology, indicating that the corrosion in the heat affected zone was more serious.