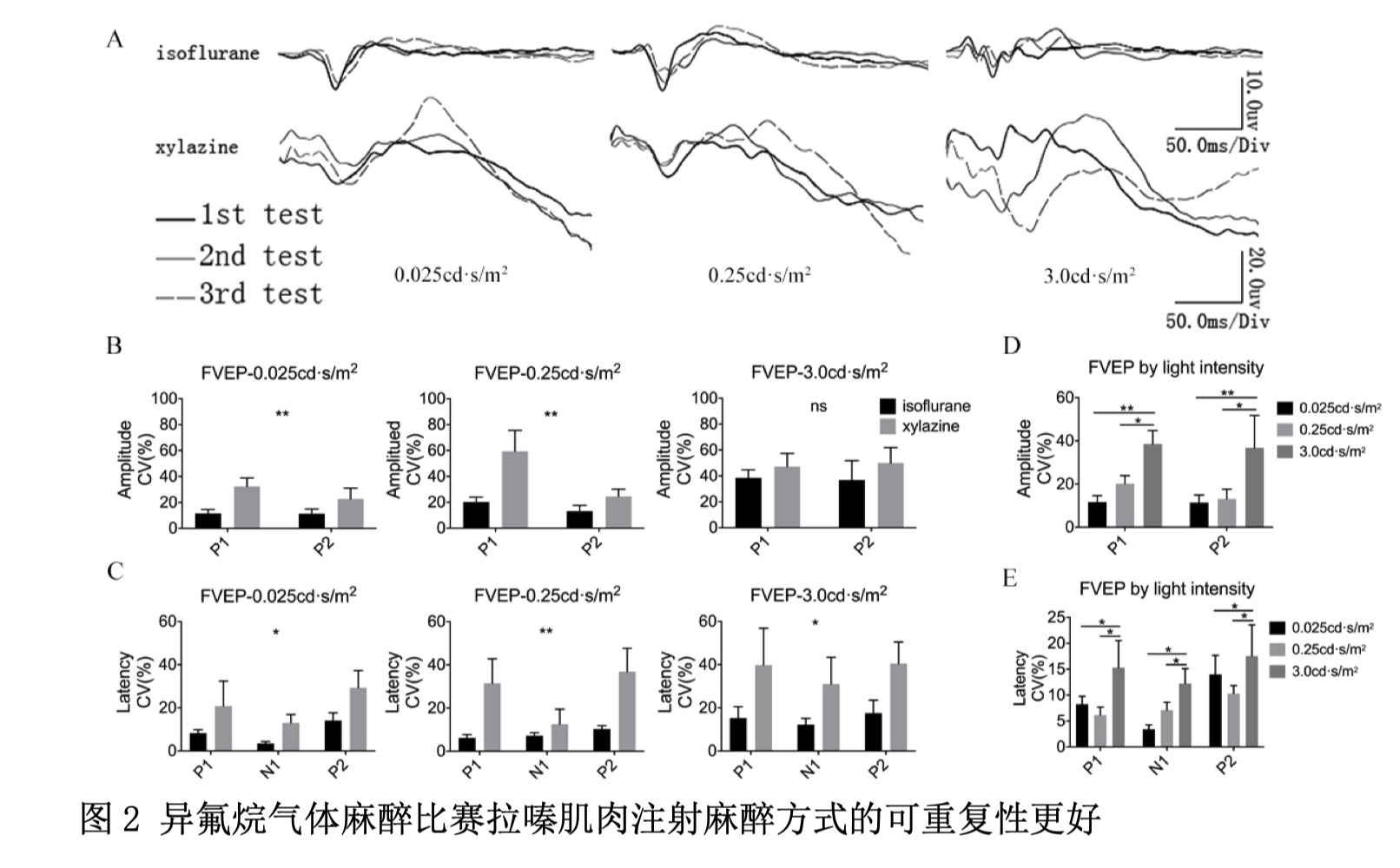
在动物身上进行电生理测试时,麻醉是必要的,以稳定信号。异氟烷和塞拉嗪都被广泛用于麻醉动物。此前的研究发现,这两种麻醉药可能对神经网络产生不同的作用,从而表现出不同的电生理特征。图2A显示了异脲或吡嗪麻醉后连续几天(间歇期)山羊FVEP波形的叠加图。Quanti !用不同光强下的间歇期变异系数(CV)进行测定,结果表明,用异氟烷记录的FVEP是显著的。在振幅和潜伏期上,均明显比在塞拉嗪时稳定。从图2B中,我们还可以注意到在3.0 cd s/m2光强下的FVEP比在0.025和0.25 cd s/m下的FVEP变化更大,这是通过统计分析fvep在不同光强振幅下的间歇CV和潜伏期
Anesthesia is necessary when perform electrophysiological tests in animals to stabilize the signal. Both isoflurane and xylazine are widely used to anesthetize animals. Previous study has found that these two anesthetics may exert different effiects on neural network, and thus exhibit distinct electrophysiological features . Fig.presented overlays of FVEP waveforms recorded on different days (intersession) from an individual goat with either iso- flurane or xylazine anesthesia. Quantification of intersession coeffcient of variation (CV) at different light intensities shown that the FVEP re- cording with isoflurane was significantly more stable than that with xylazine both in amplitude and in implicit time . From Fig, we could also notice that the FVEP at light intensity of 3.0 cd s/m2 was more variable than those at 0.025 and 0.25 cd s/m , which was confirmed by statistical analysis of the intersession CV of FVEPs among different light intensities in amplitude and implicit time