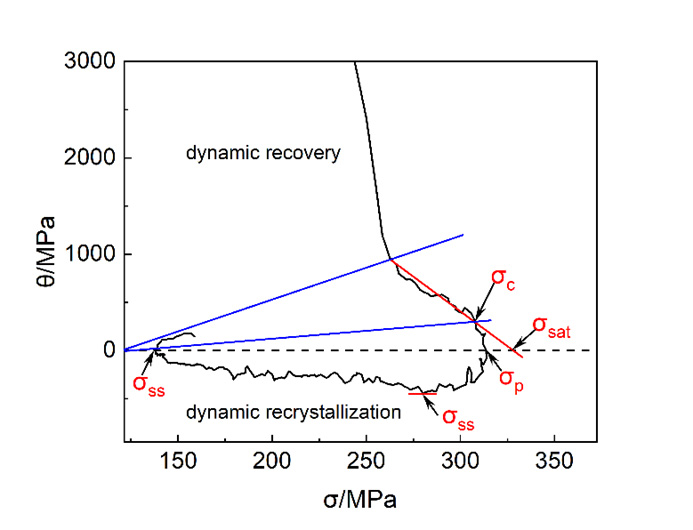
选取三种氧含量分别为140ppm、280ppm、410ppm的FGH96高温合金为材料,按Φ10×15mm加工成热压缩试样,使用电子分析天平精确称重,确保试样质量符合实验要求。将高温合金试样放置在Gleeble热模拟实验机上,在不同温度(1040℃、1070℃、1100℃、1140℃)和应变速率(0.001 s⁻¹、0.01 s⁻¹、0.1 s⁻¹、1 s⁻¹)条件下进行热压缩实验,记录每个条件下的流变应力曲线。根据应力-应变数据,计算应力对应变求积分得出加工硬化速率 (θ),利用origin得出加工硬化速率 (θ) 和应力 (σ) 的相关性。对比分析不同温度条件下材料的加工硬化行为,获得合金的加工硬化特性。
Three types of FGH96 superalloys with oxygen contents of 140ppm, 280ppm and 410ppm respectively were selected as materials and processed into hot-compressed samples with diameters of Φ10×15mm. The samples were precisely weighed using an electronic analytical balance to ensure that the sample quality met the experimental requirements. The superalloy specimens were placed on the Gleeble thermal simulation testing machine. Thermal compression experiments were conducted under different temperatures (1040℃, 1070℃, 1100℃, 1140℃) and strain rates (0.001 s⁻¹, 0.01 s⁻¹, 0.1 s⁻¹, 1 s⁻¹), and the rheological stress curves under each condition were recorded. Based on the stress-strain data, calculate the integration of stress with strain to obtain the work hardening rate (θ), and use origin to obtain the correlation between the work hardening rate (θ) and stress (σ). By comparing and analyzing the work hardening behavior of materials under different temperature conditions, the work hardening characteristics of alloys are obtained.