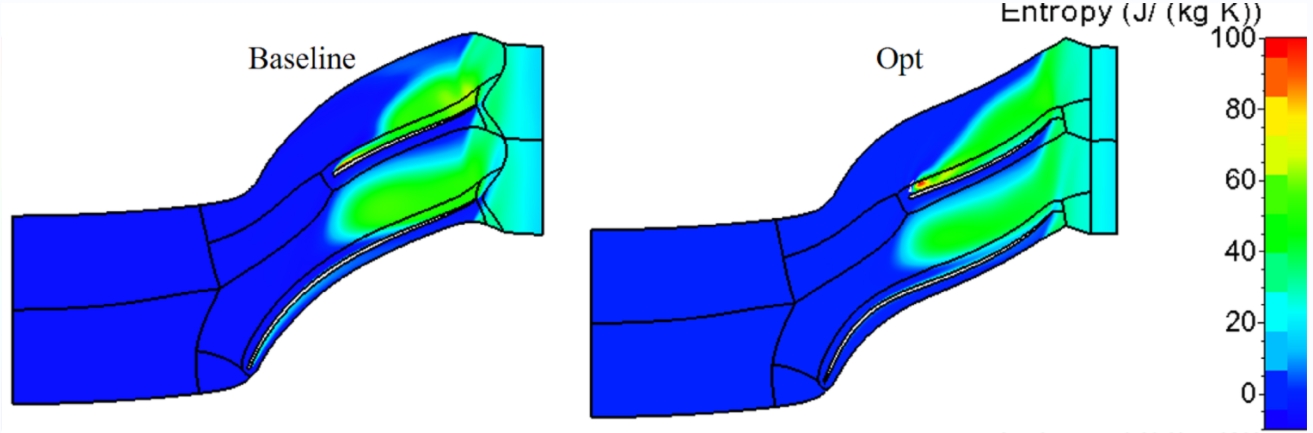
初始方案85%流道高度位置流场中存在流动附着现象,附着流体横向迁移之后又在叶轮出口位置发生分离,流动分离产生损失。优化方案发附着流体横向迁移程度增加,流线在叶片吸力面壁面附近汇聚,使得流道中部位置熵的峰值增加,由分流叶片吸力面和主叶片压力面构成的流道要比由分流叶片压力面和主叶片吸力面构成的流道中部熵增程度大。但优化方案流线在出口位置的流动分离现象减弱,流道出口位置熵值降低,由于出口熵值的降低,优化方案比初始方案效率更高。
In the initial scheme, there is flow adhesion phenomenon in the flow field at 85% of the flow channel height, and the attached fluid separates at the impeller outlet after transverse migration, resulting in flow separation loss. In the optimization scheme, the lateral migration degree of the attached fluid increases, and the flow lines converge near the blade suction surface, which increases the peak entropy at the middle of the flow channel. The flow channel formed by the suction surface of the diverter blade and the pressure surface of the main blade increases more than the middle of the flow channel formed by the pressure surface of the diverter blade and the suction surface of the main blade. However, the flow separation phenomenon of the flow line at the outlet of the optimized scheme is weakened, and the position entropy of the outlet of the flow channel is reduced. Due to the decrease of the outlet entropy, the optimized scheme is more efficient than the initial scheme.