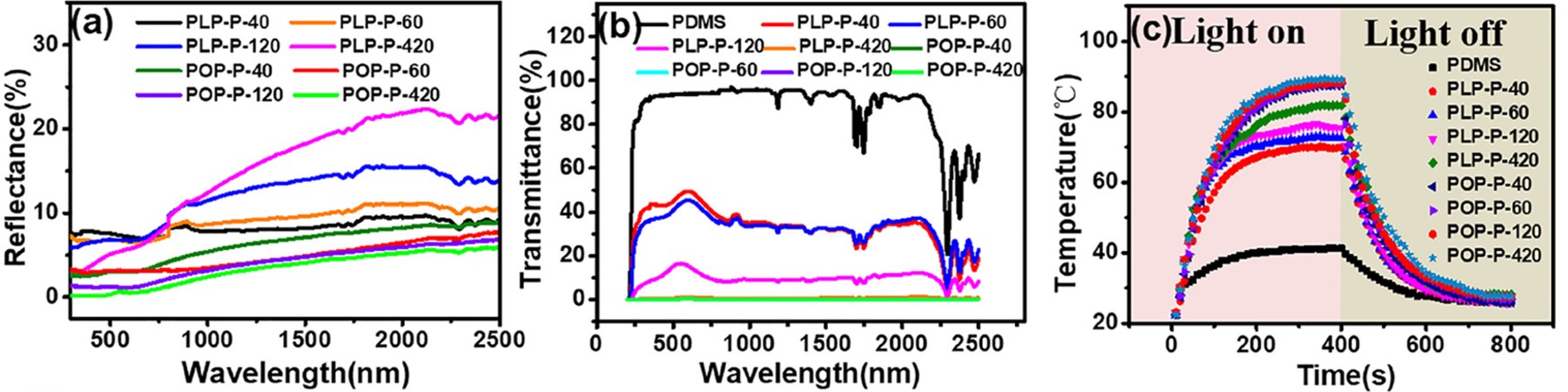
图 3a 显示了各种 PLP-P 和 POP-P 薄膜在 295-2500 纳米范围内的反射光谱测量结果,这与太阳辐照光谱范围一致。POP-P 薄膜的反射率明显低于 PLP-P 薄膜。对于 POP-P,反射率随 tp 的增加而逐渐降低,当 tp 超过 120 分钟时,反射率几乎保持不变。POP-P-120 在紫外-可见光(UV-vis)区域的平均反射率小于 5.32%,在近红外(NIR)区域的平均反射率小于 3.16%。如图 3b 所示,所有 POP-P 薄膜的透射率都近似为零。POP-P 薄膜的低反射和低透射率确保了其出色的光吸收能力,从而实现了高效的太阳能热转换。因此,在所有 PDMS/PPy 样品中,POP-P 薄膜具有更高的增温效果(图 3c)。
Figure 3a shows the reflection spectra measurements for various PLP-P and POP-P films in the range of 295–2500 nm, which is consistent with the solar irradiance spectrum ranges. The POP-P films attained significantly lower reflectance than the PLP-P films. For POP-P, the reflectance gradually decreased with an increase of tp, then almost unchanged when tp was more than 120 min. The average reflectivity of POP-P-120 was <5.32% in the ultraviolet–visible (UV–vis) region and <3.16% in the near-infrared (NIR) region. The transmittance of all of the POP-P films reached an approximate zero as shown in Figure 3b. The low reflection and transmission of POP-P films ensures outstanding light absorption, thus leading to efficient solar to heat conversion. Consequently, the POP-P films exhibited higher temperature enhancement among all of the PDMS/PPy samples (Figure 3c).