用pH7.4或6.5将每组的三个基质浸入5mL的PBS溶液中。在37C孵化时间(0、6、12、24、48、72、120和168h)后,逐个收集整个液体,并进一步加入新的PBS溶液(5mL)。分别用纳米滴一微体积紫外-可见分光光度计(美国ThermoFisher科学公司)和原子吸收光谱仪(中国西安AA-7003)对DHTA和金属离子(Zn2+和Mg2+)进行了检测。
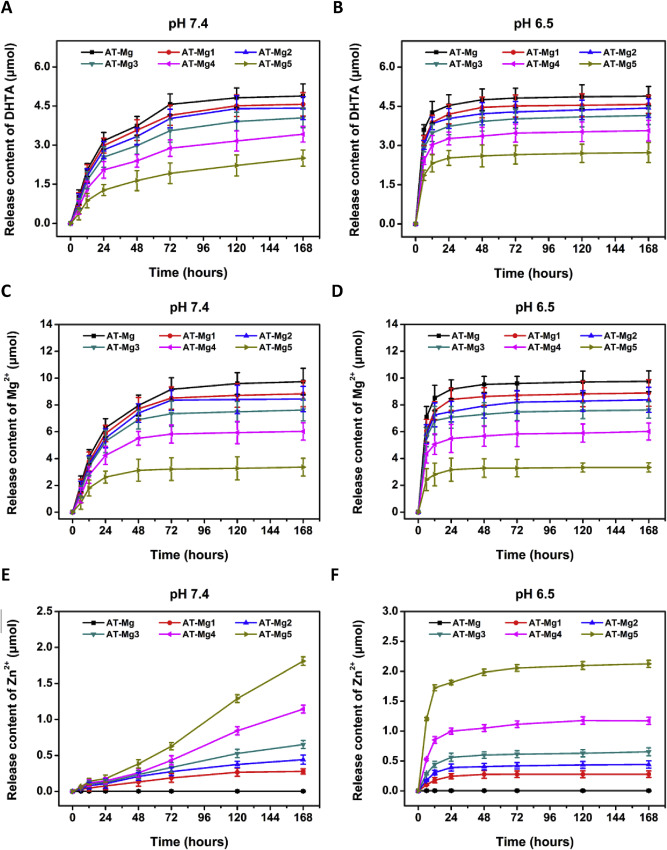
在生理(pH7.4)或酸性(pH6.5)微环境下DHTA、Mg2+、Zn2+的释放如图3所示。结果发现,在pH6.5条件下,Mg/Zn-MOF74涂层在24小时内几乎完全降解(图3B,D,F)。而在pH7.4下72小时有少量残留物(图3A,C,E)。在6h浸泡在下pH溶液中的组明显可见爆炸释放(约70%),分别计算得AT-Mg, AT-Mg/Zn1, AT-Mg/Zn2, AT-Mg/Zn3, AT-Mg/Zn4 and AT-Mg/Zn5各个样本 (1 cm2 )的DHTA (4.9, 4.6, 4.4, 4.1, 3.5, 2.7 μmol),Mg2+ (9.8, 8.9, 8.4, 7.4, 6.0, 3.3 μmol) 和Zn2+ (0, 0.3, 0.4, 0.7, 1.2, 2.1 μmol)总量。
Three substrates in each group were immersed into 5 mL of PBS solution with pH 7.4 or 6.5. After incubation for difffferent time (0, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 120, and 168 h) at 37 °C, whole liquid was collected one by one, and new PBS solution (5 mL) was further added. The detections of DHTA and metal ions (Zn2+ & Mg2+) were performed with an NanoDrop One Microvolume UV–Vis Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientifific, USA) at 352 nm and atomic absorption spectrometer (AA-7003, Xian, China), respectively.
The release of DHTA, Mg2+ and Zn2+ under physiological (pH 7.4) or acidic (pH 6.5) microenvironment was displayed in Fig. 3.It was found that Mg/Zn-MOF74 coatings were almost completely degraded within 24 h under pH 6.5 (Fig. 3B, D, F) while had a small amount of residue at 72 h under pH 7.4 (Fig. 3A, C, E ). The burst release (about 70%) was obviously observed in groups that immersed in the lower pH solution at 6 h. In AT-Mg, AT-Mg/Zn1, AT-Mg/Zn2, AT-Mg/Zn3, AT-Mg/Zn4 and AT-Mg/Zn5 groups, the total amounts of DHTA (4.9, 4.6, 4.4, 4.1, 3.5, 2.7 μmol), Mg2+ (9.8, 8.9, 8.4, 7.4, 6.0, 3.3 μmol) and Zn2+ (0, 0.3, 0.4, 0.7, 1.2, 2.1 μmol) for each specimen (1 cm2 ) were calculated, respectively.