(南京航空航天大学飞行器先进设计技术国防重点学科实验室,南京,210016)
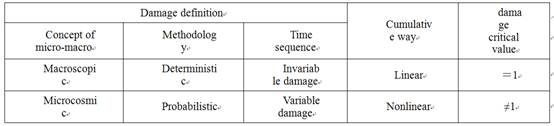
摘要:在工程实际中,疲劳破坏是引起机械系统或构件失效的主要原因之一。疲劳累积损伤理论对疲劳寿命估计十分重要。本文提出一种新的分类方式,见表1,根据疲劳累积损伤理论的三要素损伤定义、损伤累积方式和损伤临界值,撇开物质观和方法论,将主要的线性累积疲劳损伤理论分为四类;(1) 线性等损伤疲劳累积损伤理论;(2) 线性变损伤累积理论;(3) 线性等损伤分阶段疲劳累积损伤理论;对每类理论分别从理论基础、材料常数、引入的参量等方面进行分析,归纳出主要模型。
| 损伤定义 | 累加方式 | 损伤临界值 | ||
| 物质观 | 方法论 | 时序性 | ||
| 宏观 | 确定性 | 等损伤 | 线性 | =1 |
| 微观 | 不确定性 | 变损伤 | 非线性 | ≠1 |
(1)线性等损伤模型中,Miner准则在随机谱下,临界损伤值最接近于1,寿命估算准确率优于其他模型;对于有一定谱型的载荷谱,相对Miner模型寿命估算准确率则较高,Miner准则误差则可达10倍;
(2)线性等损伤分阶段模型考虑了损伤发展的阶段性特征,Manson两阶段模型相对简单,考虑了加载顺序的影响;虽然还不完备,但在工程上已有较多的应用。
(3)线性变损伤模型中,Corten-Dolan模型应用最为广泛;幂指数寿命计算模型在两级谱、块谱下应用简便,应用也较多,但随机谱应用时较为复杂;而寿命曲线修正模型、损伤力学模型、基于能量法的模型等参量定义模糊、计算繁琐,应用具有局限性;
(4)实验数据寿命预测值表明,在两级阶梯谱下,Manson准则的预测精确度最好,且两级加载下公式较为简单,无需额外确定参数,但是在高应力影响较大时,Corten-Dolan准则较为适用,但针对不同材料和载荷谱d的取值需进一步研究;多级块谱加载下,Manson准则的计算已较为复杂,而Miner准则更为简易方便,且Miner准则的精度不输于Manson准则和Corten-Dolan准则;随机谱下,Manson准则、Corten-Dolan准则或计算过程繁琐、或寿命预测值与真实寿命相差较大,而Miner准则计算简单而精确度好,因而最合适。另外由于实际工程结构的载荷谱的峰谷值的大小和顺序的随机的,Manson准则和Corten-Dolan准则不能处理这种情况。
关键词:疲劳累积损伤理论;载荷谱型;疲劳寿命估算
(Key Laboratory of Fundamental Science for National Defense-Advanced Design Technology of Flight Vehicle, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
In this thesis, a new classification method was introduced (see table 1)。 According to the three elements of cumulative fatigue damage theory: damagedefinition, cumulative way and damage critical value,the linear fatigue accumulative damage theories for metal materials were divided into the following three categories: (1) linear cumulative damage theories of Invariable damage; (2) linear cumulative damage theories of variable damage; (3)periodicallinear cumulative damage theories of Invariable damage; In this paper, the above three categories were reviewed respectively in aspects of theoretical basises, material constants, parameters introduced, etc. and major typical models were listed.
Besides, several sets of variable loading tests ofmetal materials under two-level spectrum, multiple-level spectrum and random spectrum were used to verify the major typical models. The life prediction accuracy rates of the above mayor typical models under different loading spectrum were listed. Finally, the applicable scopes and application effects of the above four kinds of accumulative damage rules were compared and discussed according to theoretical basisand the accuracy rate for the choices of engineeringapplication. Conclusions are as follows:
(1)In linear theories of Invariable damage, under random spectrum, the damage critical value of Miner Model is closest to 1 and thefatigue life prediction accuracy rate is superior to other models; under spectrums with specific patterns, thefatigue life prediction accuracy rate of Relative Miner Model is superior and the deviation of Miner model is up to 10.
(2)Periodical linear cumulative damage theories of Invariable damageincludeperiodical characteristics of the damage development. Manson's double linear model considering effects ofloading sequenceis relatively simple; although it is still not complete, this model is widely used in practical projects.
(3)In linear cumulative damage theories of variable damage, fatigue life prediction of Corten-Dolan Model is most widely used in practical projects; power-exponent function model is convenient to use and accuracy rate is close to Corten-Dolan Model; models based on S-N curve modification, continuum damage mechanic models and models based on energy have major defects such as fuzzy parameterdefinitions, complicated calculations and narrow applicable scopes, etc
(4)According to life prediction using experimental data ,several concludes are made. (a) Under two-level spectrums the prediction accuracy of Manson's double linear model is best and the formula is simple and has no extra parameter. When high stress influence is obvious, Corten-Dolan Model is more applicable but the parameter d needs more consideration under different materials . (b) Under multiple-level spectrums, Manson's model is more complex than Miner model and Corten-Dolan model and Miner model has the simplest fomula. Besides Miner model's prediction accuracy is the same as Manson's model and Corten-Dolan model. (c) Under random spectrums, Miner model with the advantage of simple formula and higher life prediction accuracy ratesis more suitable than Manson's model and Corten-Dolan model. BesidesManson model and Corten-Dolan modelcan nothandle the situation that the load spectrum peak values and the order of the spectrums are random in practical engineering structures.
Key words:Fatigue cumulative damage, Loadspectrum, Fatigue life prediction
联系方式





















