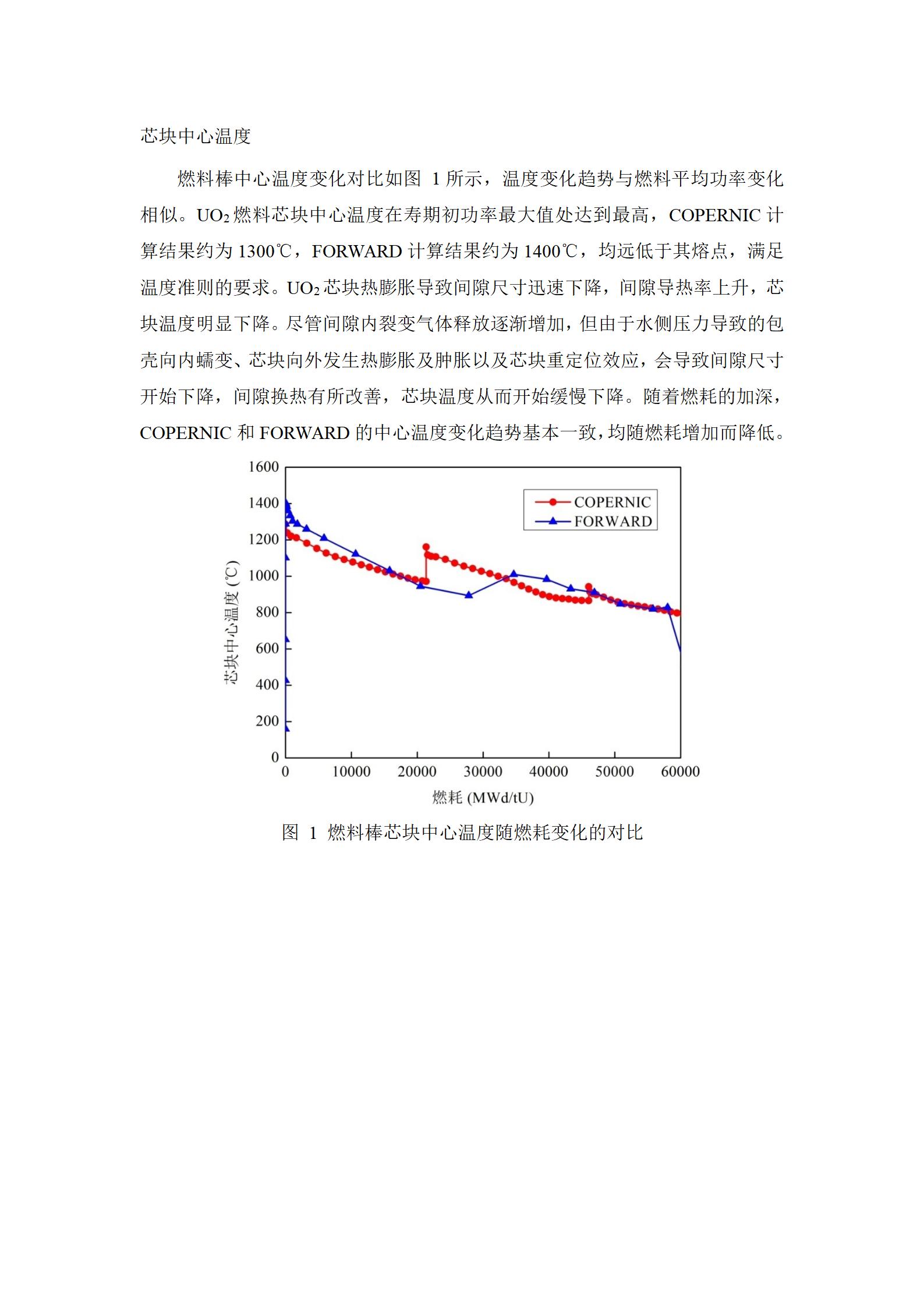
燃料棒中心温度变化对比如图 1所示,温度变化趋势与燃料平均功率变化相似。UO2燃料芯块中心温度在寿期初功率最大值处达到最高,COPERNIC计算结果约为1300℃,FORWARD计算结果约为1400℃,均远低于其熔点,满足温度准则的要求。UO2芯块热膨胀导致间隙尺寸迅速下降,间隙导热率上升,芯块温度明显下降。尽管间隙内裂变气体释放逐渐增加,但由于水侧压力导致的包壳向内蠕变、芯块向外发生热膨胀及肿胀以及芯块重定位效应,会导致间隙尺寸开始下降,间隙换热有所改善,芯块温度从而开始缓慢下降。随着燃耗的加深,COPERNIC和FORWARD的中心温度变化趋势基本一致,均随燃耗增加而降低。
The comparison of fuel rod center temperature changes is shown in Figure 1, and the temperature change trend is similar to the average fuel power change. The center temperature of UO2 fuel pellet reaches the highest at the maximum power at the beginning of its service life. The COPERNIC calculation result is about 1300 ℃, and the FORWARD calculation result is about 1400 ℃, both far below its melting point, meeting the requirements of the temperature criterion. The thermal expansion of UO2 pellets leads to a rapid decrease in gap size, an increase in gap thermal conductivity, and a significant decrease in pellet temperature. Although the release of fission gas in the gap gradually increases, due to the inner creep of the cladding caused by the water side pressure, the outward thermal expansion and swelling of the pellets, and the repositioning effect of the pellets, the gap size will begin to decline, the gap heat transfer will be improved, and the pellet temperature will begin to slowly decline. With the deepening of fuel consumption, the change trend of the center temperature of COPERNIC and FORWARD is basically the same, and both decrease with the increase of fuel consumption.