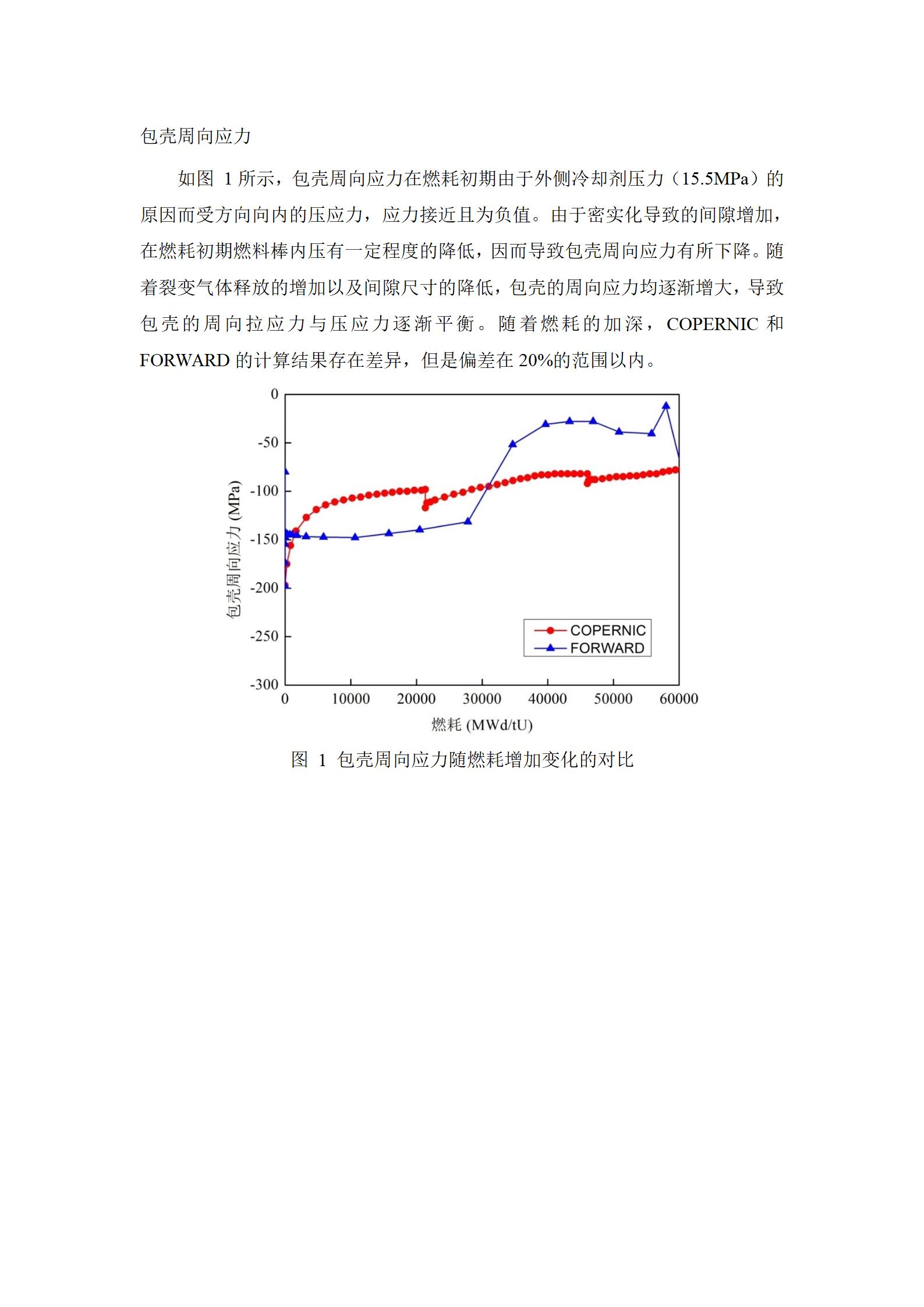
如图 1所示,包壳周向应力在燃耗初期由于外侧冷却剂压力(15.5MPa)的原因而受方向向内的压应力,应力接近且为负值。由于密实化导致的间隙增加,在燃耗初期燃料棒内压有一定程度的降低,因而导致包壳周向应力有所下降。随着裂变气体释放的增加以及间隙尺寸的降低,包壳的周向应力均逐渐增大,导致包壳的周向拉应力与压应力逐渐平衡。随着燃耗的加深,COPERNIC和FORWARD的计算结果存在差异,但是偏差在20%的范围以内。
As shown in Figure 1, the circumferential stress of the cladding is subject to the inward pressure stress due to the external coolant pressure (15.5MPa) at the initial stage of burnup, and the stress is close to and negative. Due to the increase of clearance caused by densification, the internal pressure of fuel rod decreases to a certain extent at the initial stage of burnup, which leads to the decrease of circumferential stress of cladding. With the increase of fission gas release and the decrease of gap size, the circumferential stress of the cladding increases gradually, leading to the gradual balance of the circumferential tensile stress and compressive stress of the cladding. With the deepening of fuel consumption, the calculation results of COPERNIC and FORWARD are different, but the deviation is within 20%.