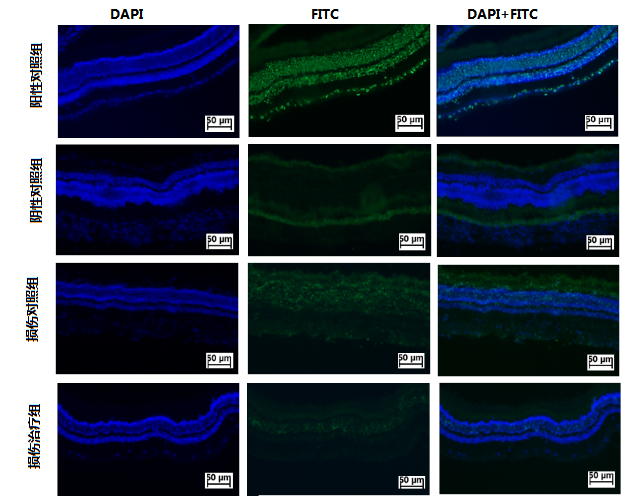
取雄性健康大耳白兔9只,随机抽取3只作为正常组(不作任何处理);其余6只兔于球后3 mm处用同一反向动脉夹夹闭视神经30 s,建立视神经损伤的动物模型。 并随机抽取3只在视神经损伤处给予0.2 mL壳聚糖温敏凝胶(FK506 1.76 μg/mL,CNTF 2 μg/mL)作为损伤治疗组,另3只为损伤对照组(0.2 mL PBS 处理)。视神经损伤14 d后,进行视网膜和视神经的HE染色,观察组织形态,行视网膜的冰冻切片,记录视网膜上RGC的凋亡情况,验证包载FK506和CNTF的水凝胶能否促进视网膜上损伤的RGC存活。
Nine healthy male big-eared white rabbits were randomly selected as the normal group (without any treatment).The other 6 rabbits were used to clamp the optic nerve 3 mm behind the bulbar for 30 s to establish the animal model of optic nerve injury.Three rats were randomly selected and treated with 0.2 mL chitosan temperature-sensitive gel (FK506 1.76 μg/mL, CNTF 2 μg/mL) as injury treatment group and the other three rats were treated with 0.2 mL PBS as injury control group.After 14 days of optic nerve injury, HE staining of the retina and optic nerve was performed to observe the tissue morphology. Frozen section of the retina was performed to record the apoptosis of RGC on the retina, and to verify whether the hydrogel containing FK506 and CNTF could promote the survival of RGC on the retina injury.