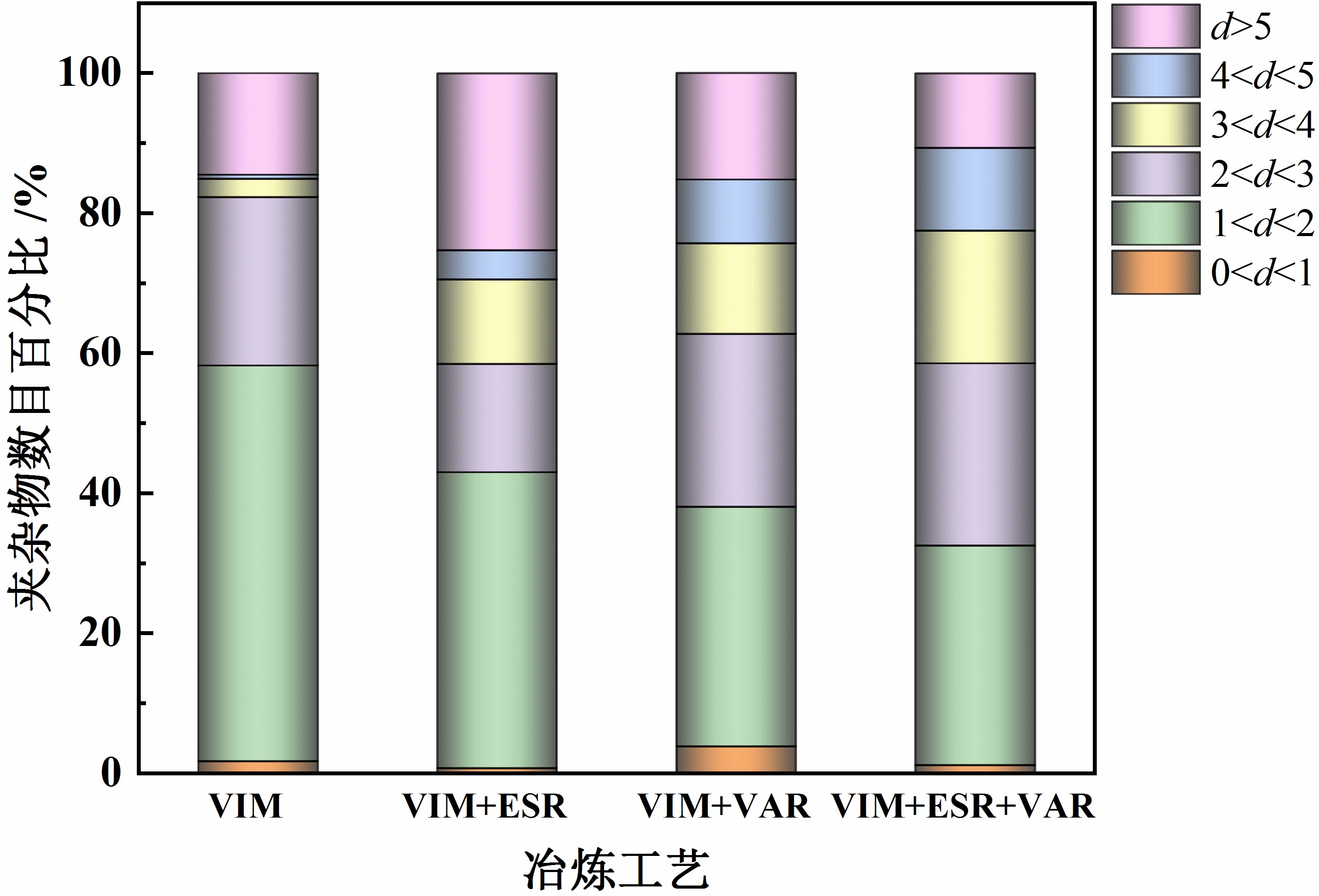
钢锭中小尺寸小于2 µm夹杂物逐渐减少,同时大于5 µm的大尺寸夹杂物也逐渐减少,但是3 µm左右反而略有增加。这是因为在电渣重熔和真空自耗过程中,液态金属与渣池充分反应,自耗电极中的大部分夹杂物被有效去除。而且在钢锭凝固过程中,结晶自下而上,也有利于部分小夹杂物的上浮而被去除。这是由于钢锭的凝固速度快,夹杂物的长大受到抑制,细小的夹杂物不易聚合长大,从而使得钢锭中的夹杂物更加均匀、细小弥散,所以大部分夹杂物聚集在3 µm左右。
The small and medium-sized inclusions less than 2 µm in the steel ingots gradually decrease, while the large-sized inclusions larger than 5 µm also gradually decrease, but they increase slightly around 3 µm. This is because in the process of electroslag remelting and vacuum consumable, the liquid metal fully reacts with the slag pool, and most of the inclusions in the consumable electrode are effectively removed. Moreover, during the solidification of the steel ingot, the crystals are from bottom to top, which is also conducive to the floating and removal of some small inclusions. This is because the solidification speed of the steel ingot is fast, the growth of inclusions is inhibited, and the small inclusions are not easy to aggregate and grow up, which makes the inclusions in the steel ingot more uniform and finely dispersed, so most of the inclusions gather around 3 µm.