在图1(a)~(d)中,随着SiO2添加量的不同,Al和Ti的含量有很大的变化。S0渣系条件下,Al和Ti的氧化率分别仅为6.98%和2.33%;S1渣系条件下,Al和Ti的氧化速率分别提高到18.39%和10.24%;S2渣系条件下,Al和Ti的氧化率分别为33.33%和15.08%;S3渣系条件下,Al和Ti的氧化率分别为44.95%和19.51%。因此,随着渣系中SiO2含量的增加,Al、Ti氧化加重,且相比,Al的氧化速率要高得多(约为2倍)。
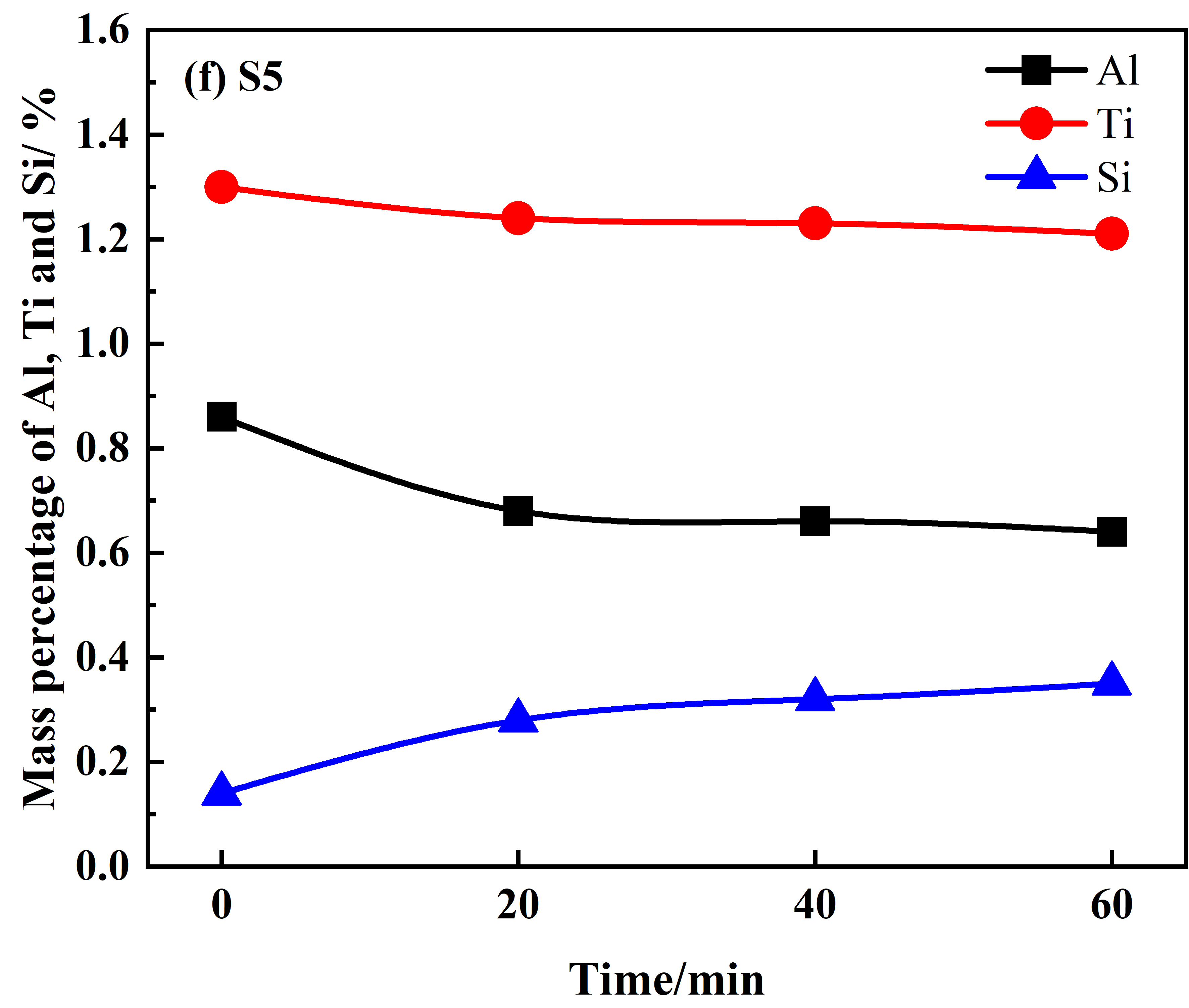
S2和S4渣样之间的最大差异是CaO含量,如图1(c)和(e)。当CaO含量从20%增加到30%时,Al和Ti的氧化率分别从33.33%和15.08%降低到21.59%和11.72%。研究表明,CaO会显著降低SiO2的活性,因此Al和Ti的氧化速率随着CaO含量的增加而降低。S1和S5渣样之间的最大差异是TiO2含量,如图b和f。当TiO2含量从4%增加到8%时,Ti的氧化率从10.23%下降到6.92%,Al的氧化率从18.39%上升到25.58%。
In Fig. 1(a)~(d), the contents of Al and Ti vary greatly with the addition of SiO2. Under the condition of S0 slag system, the oxidation rates of Al and Ti are only 6.98% and 2.33% respectively; Under the condition of S1 slag system, the oxidation rates of Al and Ti increase to 18.39% and 10.24% respectively; The oxidation rates of Al and Ti are 33.33% and 15.08% respectively in S2 slag system; The oxidation rates of Al and Ti are 44.95% and 19.51% respectively in S3 slag system. Therefore, with the increase of SiO2 content in the slag system, the oxidation rate of Al and Ti is increased, and the oxidation rate of Al is much higher than that of Al (about 2 times).