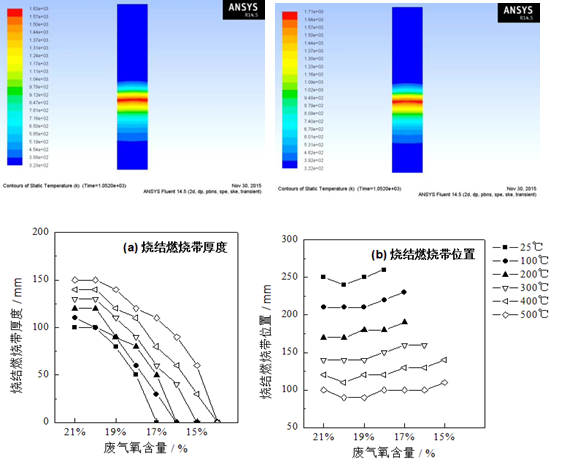
烧结燃烧带随烟气温度提高而变厚,随烟气氧含量下降而变窄,与理论推测结果一致。当氧含量高于19%时,所有温度下烧结燃烧带均与正常值相当或厚于正常值;当氧含量为18%时,需要烟气温度在300℃以上才能确保燃烧带厚度达到正常值水平;当氧含量17%时,烧结燃烧带收缩至正常值的60%以下,将对烧结矿质量带来负面影响;烟气氧含量进一步降至16%以下时,烧结燃烧带进一步缩小直至消失,烧结矿质量将无法得到保证。由烧结燃烧带位置来看,提高烧结烟气温度将使燃烧带上移;提高烟气含氧量后燃烧带下移,与料层温度最高点(燃烧带中心点)移动方向相反。主要是由于烧结燃烧带位置为燃烧带起始点位置,虽然烟气氧含量降低后燃烧带中心点上移,但氧含量降低使燃烧带变窄带来燃烧带起始点下移。
The sintering zone thickens with the increase of flue gas temperature, and becomes narrower with the decrease of flue gas oxygen content, which is consistent with the theoretical prediction. When the oxygen content is higher than 19%, the sintered combustion zone is equal to or thicker than the normal value at all temperatures. When the oxygen content is 18%, the flue gas temperature should be above 300℃ to ensure that the thickness of the combustion zone can reach the normal level; When the oxygen content is 17%, the sintering combustion zone shrinks to less than 60% of the normal value, which will have a negative impact on the quality of sinter. When the oxygen content of flue gas further decreases to below 16%, the sintering combustion zone further shrinks until it disappears, and the quality of sinter cannot be guaranteed. From the position of sintering combustion zone, increasing the temperature of sintering gas will make the combustion zone move up. When the oxygen content of flue gas is increased, the combustion zone moves down, which is opposite to the movement direction of the highest temperature of the material layer (the center point of the combustion zone). The main reason is that the position of the sintering combustion zone is the starting point of the combustion zone. Although the central point of the combustion zone moves up after the oxygen content of flue gas decreases, the starting point of the combustion zone moves down as the oxygen content decreases and the combustion zone becomes narrower.