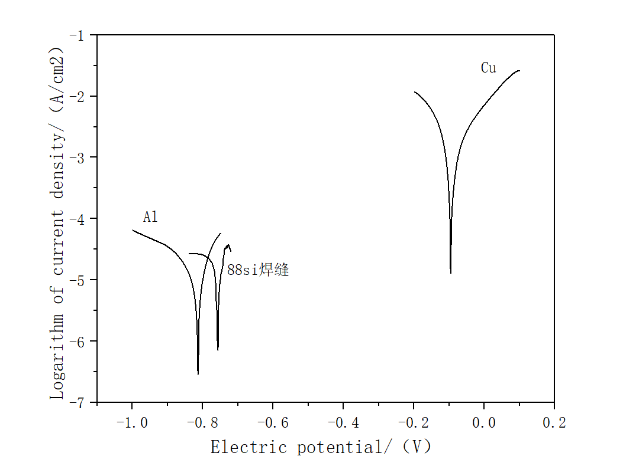
3003的腐蚀电位为-0.831V,BAl88Si钎缝金属的腐蚀电位为-0.757V、T2紫铜的腐蚀电位为-0.096V,排序可得3003的腐蚀电位最低,即在这三种材料中3003最容易被腐蚀,其次是BAl88Si钎缝金属,T2紫铜则是最不容易发生电化学腐蚀。通过腐蚀电位排序得,钎缝金属的耐腐蚀性远低于T2紫铜,表明在钎缝金属与T2紫铜之间形成的原电池中,钎缝金属电极电位低,充当阳极而最先被腐蚀。在钎缝金属与3003组成的原电池中,3003的腐蚀电位低于钎缝金属的腐蚀电位,3003充当阳极先被腐蚀。
The corrosion potential of 3003 is -0.831V, the corrosion potential of BAl88Si brazing metal is -0.757V, and the corrosion potential of T2 copper is -0.096V. Sorting can get the lowest corrosion potential of 3003, that is, 3003 is the easiest among these three materials. It is corroded, followed by BAl88Si brazing metal, and T2 copper is the least prone to electrochemical corrosion. Sorted by the corrosion potential, the corrosion resistance of the brazing metal is much lower than that of T2 copper, indicating that in the galvanic cell formed between the brazing metal and T2 copper, the electrode of the brazing metal has a low potential and acts as an anode and is the first to be corroded. In the galvanic cell composed of brazing metal and 3003, the corrosion potential of 3003 is lower than that of brazing metal, and 3003 acts as an anode to be corroded first.