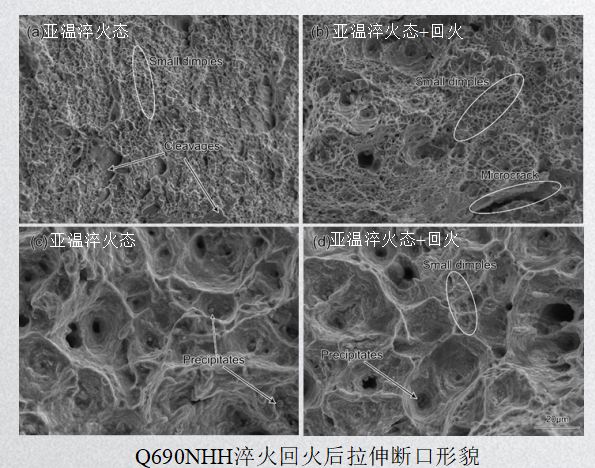
在室温下拉伸断裂时,试验钢板断口呈现大量解理面且所占面积较大,这些解理面汇聚形成河流花样,为解理断裂。在600℃下变形时,均没有解理台阶,出现了大量尺寸各异的等轴韧窝,在高温拉伸变形过程中,晶粒内部优先形成韧窝,韧窝长大聚集到一起形成颈缩,最后断裂形成微孔聚集型断口,是典型的韧性断裂。
When tensile fracture at room temperature, the fracture of the test steel plate presents a large number of cleavage surfaces and occupies a large area. These cleavage surfaces converge to form a river pattern, which is a cleavage fracture. When deforming at 600℃, there are no cleavage steps, and a large number of equiaxed dimples of different sizes appear. During high temperature tensile deformation, dimples are preferentially formed inside the grains, and the dimples grow and gather together to form a neck. It shrinks and finally fractures to form a microporous aggregated fracture, which is a typical ductile fracture.