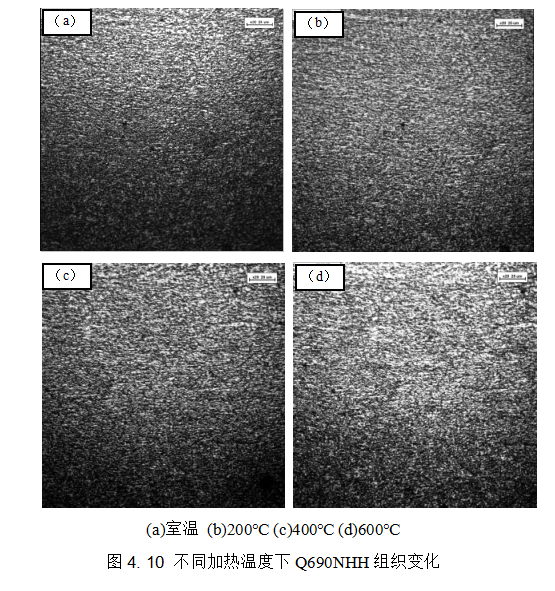
对试制钢板进行100℃-600℃加热,通过高温共聚焦显微镜观察不同温度下钢板的组织变化,金相组织见图4.10,通过图4.10可以看出随着加热温度的升高,粒状贝氏体组织逐渐增加且晶粒逐渐增大,400℃以下时组织变化不明显,当温度达到600℃时,可以明显看出贝氏体晶粒尺寸增加,晶粒尺寸的长大是导致钢板强度在600℃下降的一个重要原因。
The trial steel plate was heated at 100℃-600℃, and the microstructure changes of the steel plate at different temperatures were observed through a high-temperature confocal microscope. The metallographic structure is shown in Figure 4.10. It can be seen from Figure 4.10 that as the heating temperature increases, granular bainite The structure gradually increases and the grains gradually increase. The structure change is not obvious when the temperature is below 400°C. When the temperature reaches 600°C, it can be clearly seen that the bainite grain size increases. The growth of the grain size results in the strength of the steel plate An important reason for the drop in 600°C.