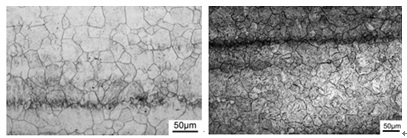
图(a)和图(b)分别为DZ2(0.05V0Nb)钢850℃一次淬火和850℃两次淬火的奥氏体晶粒形貌图,由图可知奥氏体晶粒均为等轴晶粒,通过直线截距法统计奥氏体晶粒尺寸可知,一次淬火、两次淬火时平均晶粒尺寸分别为为43 µm、23µm,两次淬火下晶粒尺寸减小20μm,细化程度为46.5%,主要原因是第一次淬火时获得的组织原奥氏体晶粒粗大,在再加热过程中,奥氏体可以在原奥氏体晶界、板条束界以及板条块界上形核,提供了更多的形核位置,因此晶粒尺寸减小。
Figure (a) and Figure (b) respectively show the morphology of austenite grains of DZ2 (0.05V0Nb) steel after quenching at 850℃ for one time and quenching at 850℃ for two times. According to the figure, all austenite grains are equiaxed grains. The average grain size of austenite grains during quenching at one time and quenching at two times is 43 µm and 23µm, respectively. The grain size is reduced by 20μm and the refinement degree is 46.5% after two quenching. The main reason is that the grain size of proto-austenite obtained during the first quenching is coarse. In the reheating process, austenite can nucleate on the grain boundary of proto-austenite, strip bundle boundary and strip block boundary, providing more nucleation sites, so the grain size is reduced.