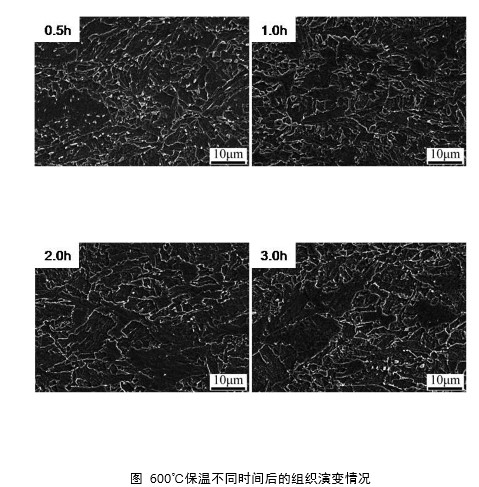
对耐蚀耐火钢进行热处理,观察600℃分别保温0.5h、1h、2h和3h后的组织演变情况,随着保温时间的延长,针状铁素体逐渐长大与合并,粒状贝氏体逐渐转变为块状铁素体,组织退化行为明显。随保温时间由0.5h延长至3.0h,MA组元的平均尺寸由0.54μm降至0.37μm,体积分数由7.0%左右降至1.0%左右,MA组元在保温过程中不断分解,无法为耐蚀耐火钢提供有效的高温强度。而针状铁素体和粒状贝氏体内部高密度位错及第二相粒子析出才能有效保证耐蚀耐火钢高温屈服强度。
The microstructure evolution of corrosion resistant refractory steel was observed after heat treatment at 600℃ for 0.5h, 1h, 2h and 3h, respectively. With the extension of holding time, acicular ferrite gradually grew up and merged, and granular bainite gradually transformed into massive ferrite, and the microstructure degradation behavior was obvious. With the increase of holding time from 0.5h to 3.0h, the average size of MA component decreases from 0.54μm to 0.37μm, and the volume fraction decreases from about 7.0% to about 1.0%. MA component is constantly decomposed during the holding process, so it cannot provide effective high temperature strength for corrosion resistant refractory steel. The high density dislocation and the precipitation of second phase particles in acicular ferrite and granular bainite can effectively guarantee the high temperature yield strength of corrosion resistant refractory steel.