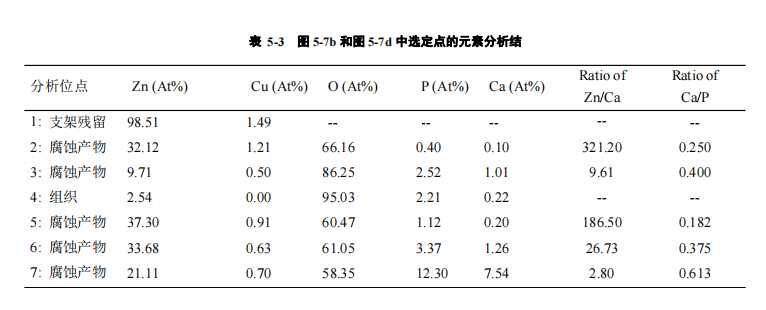
表 5-3 是图 5-7(b)和图 5-7(d)中黄点位置的元素分析结果。点 1 和点 4 分别表示支架残留物和组织。点 2、3、5、6、7 点的分析结果表明了腐蚀产物的元素
含量。点 2 代表杆件周围的初始腐蚀产物,Ca、P 含量较低,Zn、Cu 含量较高。点7 可能是典型的后续腐蚀产物,Ca、P 含量较高,Zn、Cu 含量较低。腐蚀产物中
Zn/Ca 的比值可在 321~321 的较大范围内变化。这些结果表明,随着降解过程的进行,磷酸钙被取代为磷酸锌。在最富钙的腐蚀产物(在第 7 点观察到)中,Ca/P 的
比值为 0.613。
Table 5-3 shows the elemental analysis results of the yellow dots in Figure 5-7(b) and Figure 5-7(d). Points 1 and 4 respectively indicate stent residue and tissue. The analysis results at points 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7 indicate the element content of the corrosion products. Point 2 represents the initial corrosion products around the rod. The content of Ca and P is lower, and the content of Zn and Cu is higher. Point 7 may be a typical subsequent corrosion product, with higher Ca and P contents, and lower Zn and Cu contents. The ratio of Zn/Ca in the corrosion products can vary from 321 to 321 in a wide range. These results indicate that as the degradation process progresses, calcium phosphate is replaced with zinc phosphate. Among the most calcium-rich corrosion products (observed at point 7), the ratio of Ca/P is 0.613.