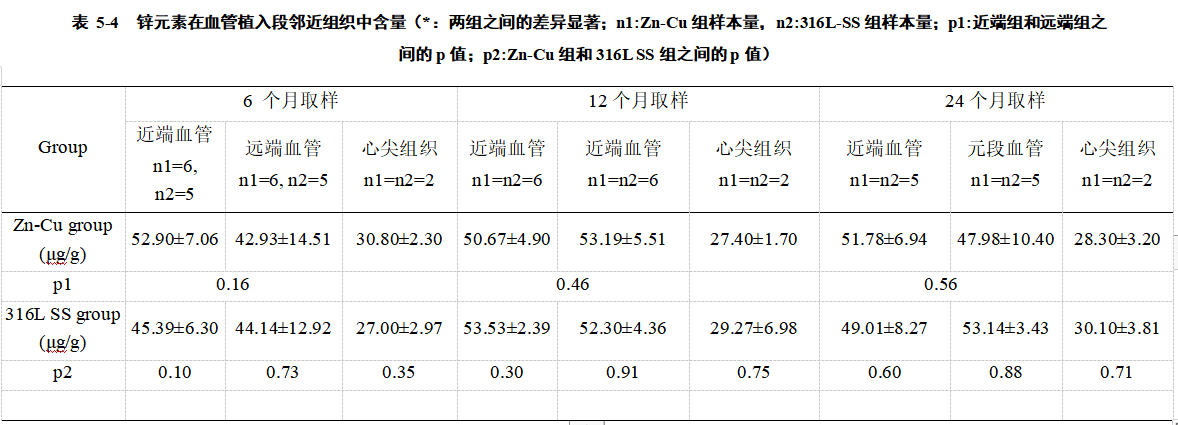
表 5-4 为支架植入术后 6、12、24 个月时,Zn 元素在植入段血管近端 5 mm 处血管、远端 5 mm 处血管和心尖部位组织的含量。两组之间的差异显著;n1:Zn-Cu 组样本量,n2:316L-SS 组样本量;p1:近端组和远端组之 间的 p 值;p2:Zn-Cu 组和 316L SS 组之间的 p 值。表 5-4 显示,无论 Zn-Cu 组与对照组之间吗,或者是植入段血管的远端与近端之间,锌元素的含量均无显著差异。作为人体必需元素,婴儿的膳食锌摄入量为 2 mg/d,成年人为 14 毫克/ 天[56]。锌铜支架 3.0 mm×20 mm 模型的重量仅为 25 mg。血液中锌的含量为32.3 mg/kg[57],这意味着锌-铜支架植入引起的锌含量太低,理论上锌支架的植入不存引发远端脏器中锌富集的可能性。表 5-4 表明,锌铜支架的植入也不能诱导锌在邻近组织中的蓄积。离子锌在活体组织中的快速转移速率[58]可能解释了这一结果。心肌和平滑肌都属于非随意肌,能够有选择的沉积锌和铜。本研究在血管的远端、近端以及心尖组织并没有发现锌、铜含量的异常。说明两种元素进入了正常的代谢,而没有对脏器的元素含量有所影响。
Table 5-4 shows the content of Zn in the blood vessel at the proximal end of the implanted segment 5 mm, the distal end of the vessel and the apical tissue at 6, 12, and 24 months after stent implantation. The difference between the two groups is significant; n1: the sample size of the Zn-Cu group, n2: the sample size of the 316L-SS group; p1: the p-value between the proximal and distal groups; p2: the Zn-Cu group and 316L SS The p-value between groups. Table 5-4 shows that there is no significant difference in the zinc content between the Zn-Cu group and the control group, or between the distal end and the proximal end of the implanted blood vessel. As an essential element for the human body, the dietary zinc intake for infants is 2 mg/d, and for adults is 14 mg/day [56]. The weight of the 3.0 mm×20 mm model with zinc-copper bracket is only 25 mg. The content of zinc in the blood is 32.3 mg/kg[57], which means that the zinc content caused by the implantation of the zinc-copper stent is too low. Theoretically, the implantation of the zinc stent may not cause zinc enrichment in the distal organs. sex. Table 5-4 shows that the implantation of zinc-copper stents also cannot induce zinc accumulation in adjacent tissues. The rapid transfer rate of ionic zinc in living tissues [58] may explain this result. Both myocardium and smooth muscle are involuntary muscles, which can selectively deposit zinc and copper. In this study, no abnormalities in zinc and copper content were found in the distal, proximal, and apical tissues of blood vessels. It shows that the two elements have entered the normal metabolism without affecting the element content of the organs.