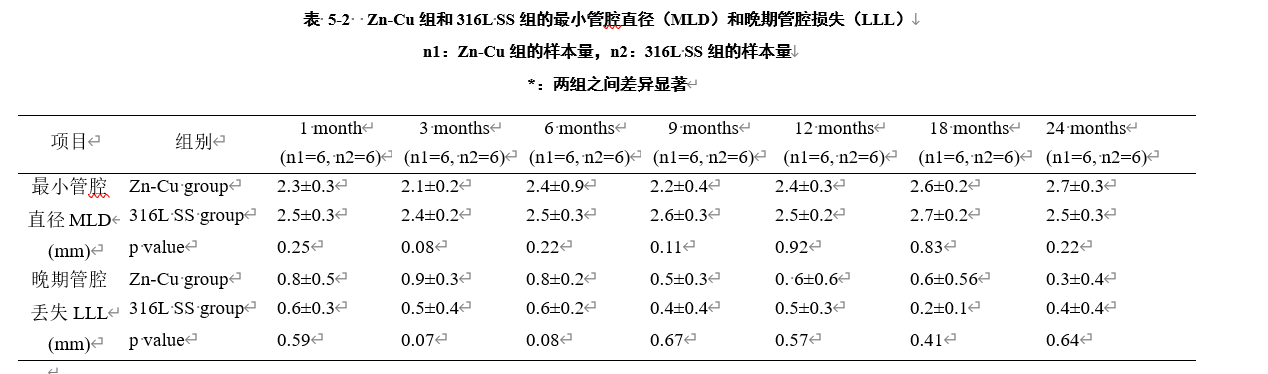
最小管腔直径(MLD)可以直接反应冠状动脉内血流情况和再狭窄进展情况:MLD值越小,代表血样的管腔越小、血流通过性越差;MLD值越大,则代表血管的通畅性越好。管腔丢失意味着血管血液通过能力的下降,因此使用MLD(LLL=MLD-(植入后瞬间直径))计算得到的晚期管腔丢失(LLL),是表征支架机械性能最重要观察手段之一。表5-2为支架植入后Zn-Cu组和316L SS组支架植入段血管内最小管腔直径及由此计算得到的晚期管腔丢失数据。 结果表明,在24个月的研究期间,Zn-0.8Cu组和316L SS组的MLD和LLL结果均无显著差异。提示锌铜支架的机械性能与316L SS支架相当。
The minimum lumen diameter (MLD) can directly reflect the blood flow in the coronary artery and the progress of restenosis: the smaller the MLD value, the smaller the lumen representing the blood sample and the worse the blood flow permeability; The greater the MLD value, the better the patency of blood vessels. Lumen loss means the decrease of vascular blood passing capacity. Therefore, the late lumen loss (LLL) calculated by MLD (LLL = MLD - (instantaneous diameter after implantation)) is one of the most important observation methods to characterize the mechanical properties of stents [28,29]. Table 5-2 and figure 5-4 show the minimum lumen diameter in the stent implantation section of Zn Cu group and 316L SS group after stent implantation and the calculated late lumen loss data.The results showed that there was no significant difference in MLD and LLL results between zn-0.8cu group and 316L SS group during the 24 month study period. It is suggested that the mechanical properties of zinc copper stent are equivalent to that of 316L SS stent.