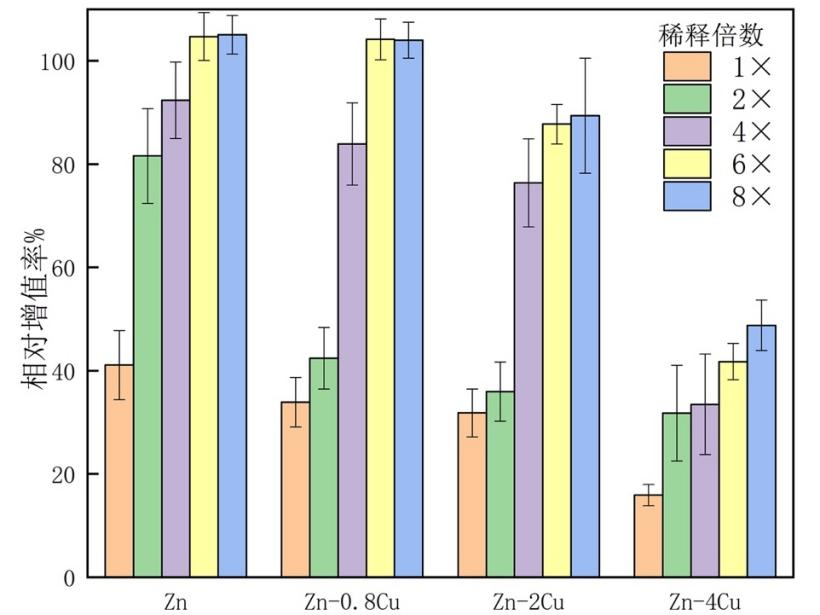
现有的医疗器械评价法规体系中,细胞毒性为0级(相对增殖率≥100%)或1级(细胞增殖率80%~99%)是可接受的。由于锌基材料的可降解性,无论纯锌或其合金,浸提液原液的细胞毒性都无法达到标准。利用稀释的方法,可以对合金的相对毒性进行评价。图3-10显示,随着铜含量的增加,锌铜合金的细胞相对增殖率下降(毒性提高),但随着浸提液浓度的稀释,相对增殖率回升,并可能超过阴性对照(Zn和Zn-0.8Cu组稀释6-8倍)。
In the existing medical device evaluation regulatory system, a cytotoxicity level 0 (relative proliferation rate ≥100%) or level 1 (cell proliferation rate 80%~99%) is acceptable. Due to the degradability of zinc-based materials, no matter pure zinc or its alloys, the cytotoxicity of the extract solution cannot reach the standard. Using the dilution method, the relative toxicity of the alloy can be evaluated. Figure 3-10 shows that with the increase of copper content, the relative cell proliferation rate of the zinc-copper alloy decreases (increased toxicity), but as the concentration of the extract is diluted, the relative proliferation rate rises, and may exceed the negative control (Zn and Zn-0.8Cu group diluted 6-8 times).