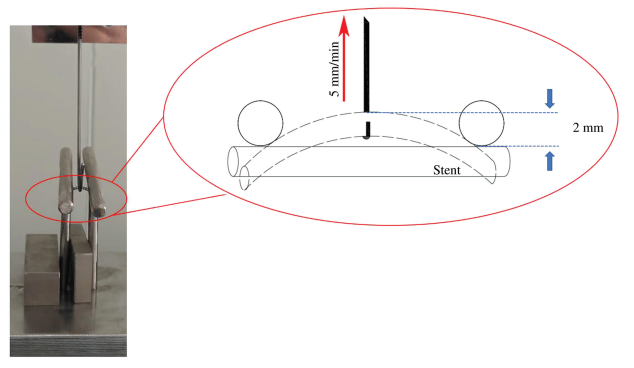
将支架弯曲力(bending force)定义为:中间点向上提升2 mm时产生的峰值拉力。测量方法参考标准ASTM-E8-04(图4-5):两个8 mm直径的平行圆棒以中心相距16 mm分隔开并固定;圆棒形成了三点弯曲试验中的两端端点。万能材料试验机(CMT4105,美特斯工业系统, 中国)上夹头固定直径约3 mm的金属钩,从支架的中间点施加垂直向上的拉力(如图4-5所示)。测试用的支架为不带输送系统、未扩张前的Zn-Cu支架和316L SS支架,型号均为3.0*20。实验组、对照组样本量均为6。Zn-Cu支架的弯曲力为0.14±0.02 N,316L SS支架的弯曲力为0.54±0.12 N。Zn-Cu支架弯曲力仅为316L SS支架的25.9%。支架弯曲力可以影响支架通过弯曲血管时难易程度:越容易弯曲则支架系统越容易通过弯曲血管、在通过血管的过程中对血管壁造成的损伤越小。另一方面,支架弯曲力的大小可以在一定程度上反映支架植入弯曲血管后,血管节段受到的支架张力。Zn-Cu支架的弯曲力更小,因此能够比316L支架更好地遵循弯曲的血管轮廓,对血管节段带来的刺激也更小(图4-19)。
The stent bending force (bending force) is defined as the peak tensile force generated when the middle point is raised 2 mm upward. The measurement method refers to the standard ASTM-E8-04 (Figure 4-5): Two parallel round bars of 8 mm diameter are separated and fixed with a center distance of 16 mm; the round bars form the two end points in the three-point bending test. A metal hook with a diameter of about 3 mm is fixed on the chuck of the universal material testing machine (CMT4105, MTS Industrial Systems, China), and a vertical upward pulling force is applied from the middle point of the bracket (as shown in Figure 4-5). The stents used in the test are Zn-Cu stents and 316L SS stents without delivery system, unexpanded, and all models are 3.0*20. The sample size of the experimental group and the control group are both 6. The bending force of the Zn-Cu stent is 0.14±0.02 N, and the bending force of the 316L SS stent is 0.54±0.12 N. The bending force of the Zn-Cu stent is only 25.9% of that of the 316L SS stent. The bending force of the stent can affect the difficulty of the stent passing through a curved blood vessel: the easier it is to bend, the easier it is for the stent system to pass through the curved blood vessel, and the less damage is caused to the blood vessel wall in the process of passing through the blood vessel. On the other hand, the bending force of the stent can reflect to a certain extent the stent tension on the vascular segment after the stent is implanted in the curved blood vessel. The bending force of the Zn-Cu stent is smaller, so it can follow the curved blood vessel contour better than the 316L stent, and it will bring less stimulation to the blood vessel segment (Figure 4-19).