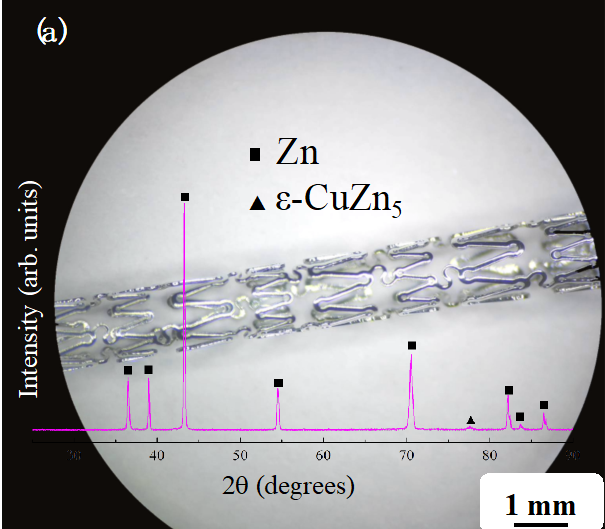
图4-15分别为Zn-Cu支架在:(a)化学抛光后、(b)压握到输送系统(SDS)上、(c)充启至标称压力和(d)球囊爆破时的形貌。要保证支架系统在生产和植入过程中能够保持其结构完整性,承受大范围的塑性变形是冠脉支架的基本要求。本研究中设计的Zn-Cu支架,在化学抛光、压握组装、扩张释放或充盈至爆破过程中的直径变化分别为1.5 mm→0.8 mm~1.0 mm→3.0 mm→3.4 mm。图4-15显示,Zn-Cu支架在压握、充启至球囊标称压力(6 atm)甚至充启至球囊破裂(24 atm)的过程中可以保持其完整性。在这些变形过程中未发现支架失效或裂纹。支架通过直径(crossing profile)与支架的壁厚设计、材料弹性和压握加工过程参数等系列因素有关,是影响支架通过血管能力的重要指标之一。本研究制备的Zn-Cu合金冠脉支架通过直径约为0.8 mm~1.0 mm(图4-15(b)),低于文献报道中可降解支架的通过直径:商用“DREAMS 2G”及“AMS-1”WE43镁合金支架为1.44 mm;经过渗氮硬化的铁支架为0.99±0.02 mm;带有锌涂层的铁支架为1.04±0.02 mm;商用“Absorb GT1 BVS”聚乳酸支架为1.38±0.01 mm。低通过直径使Zn-Cu支架具备通过更小直径血管的能力,是相比于其他可降解支架的一项重要优势。
Figure 4-15 shows the Zn-Cu stent after: (a) after chemical polishing, (b) crimped onto the delivery system (SDS), (c) inflated to the nominal pressure, and (d) balloon burst Morphology. To ensure that the stent system can maintain its structural integrity during production and implantation, it is a basic requirement for coronary stents to withstand a wide range of plastic deformation. The diameter changes of the Zn-Cu stent designed in this study during chemical polishing, crimping assembly, expansion and release, or filling to blasting process were 1.5 mm→0.8 mm~1.0 mm→3.0 mm→3.4 mm, respectively. Figure 4-15 shows that the Zn-Cu stent can maintain its integrity during the process of crimping, inflating to the balloon's nominal pressure (6 atm) or even inflating to the balloon rupture (24 atm). During these deformation processes, no failure or cracks of the stent were found. The crossing profile of the stent is related to a series of factors such as the wall thickness design of the stent, material elasticity, and compression processing parameters, and is one of the important indicators that affect the ability of the stent to pass through the blood vessel. The passage diameter of the Zn-Cu alloy coronary stent prepared in this study is about 0.8 mm~1.0 mm (Figure 4-15(b)), which is lower than the passage diameter of the degradable stent reported in the literature: commercial "DREAMS 2G" and "AMS" -1"WE43 magnesium alloy stent is 1.44 mm; iron stent hardened by nitriding is 0.99±0.02 mm; iron stent with zinc coating is 1.04±0.02 mm; commercial "Absorb GT1 BVS" polylactic acid stent is 1.38± 0.01 mm. The low pass diameter enables the Zn-Cu stent to pass through smaller diameter blood vessels, which is an important advantage over other degradable stents.