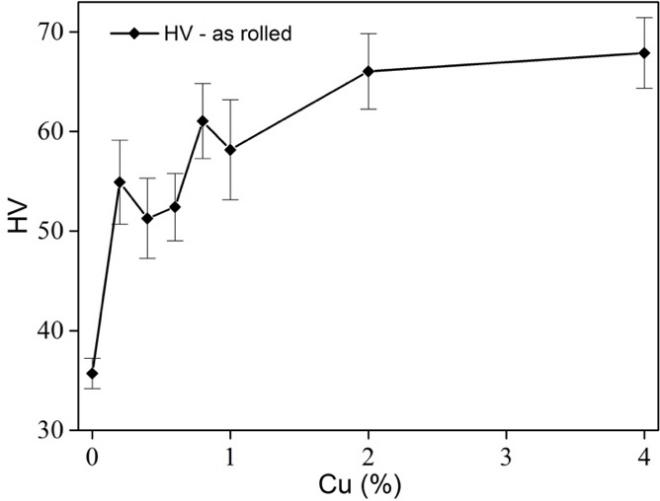
在本研究中,少量Cu的加入(0.2wt.%Cu)即显著提高了材料的硬度。图3-6显示,当铜含量低于1wt.%时,无论在XRD结果或是金相组织中都很难观察到有较大量的ε第二相的存在。当粗大的ε第二相大量出现后(铜含量大于2%),铜含量对合金硬度的提高反而不明显。这说明铜元素加入锌基底后形成的固溶体产生的固溶强化作用,对合金硬度的提高起到了关键作用。当铜含量持续提高至ε第二相产生,弥散强化所导致的硬度提升效果是有限的。
In this study, the addition of a small amount of Cu (0.2wt.% Cu) significantly increased the hardness of the material. Figure 3-6 shows that when the copper content is less than 1wt.%, it is difficult to observe the presence of a large amount of ε second phase in either the XRD results or the metallographic structure. When the coarse ε second phase appears in large quantities (the copper content is greater than 2%), the increase in the hardness of the alloy by the copper content is not obvious. This shows that the solid solution strengthening effect of the solid solution formed after the copper element is added to the zinc substrate plays a key role in the improvement of the hardness of the alloy. When the copper content continues to increase until the second phase of ε is produced, the hardness improvement effect caused by the dispersion strengthening is limited.