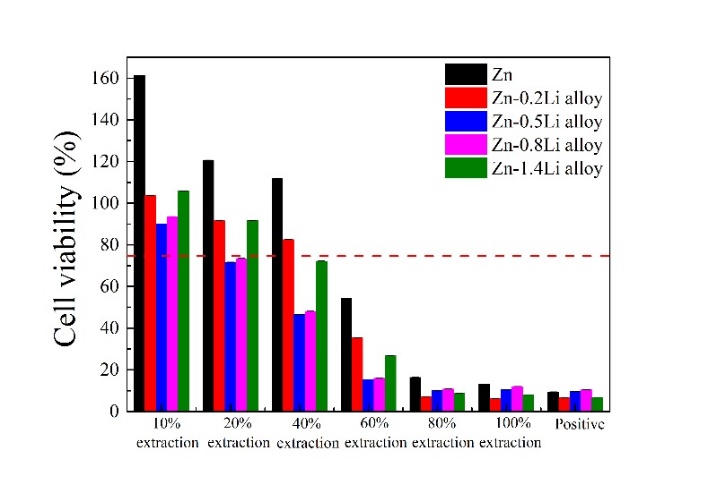
为了确定Li在ZnLi合金的细胞毒性中的作用,L-929锌和Zn-(0.2-1.4)锂合金在不同浓度的提取物中培养1天后的细胞活力如图12所示。根据ISO10993-5:1999标准,锌的提取物浓度在40%内,细胞活力超过100%促进细胞增殖。然而,当其提取物浓度超过60%时,其细胞毒性能力不超过75%。对于ZnLi合金,10%的锌(0.2-1.4)Li合金提取物无细胞毒性,Zn-0.2Li和Zn-1.4Li合金提取物可促进细胞增殖。当提取物浓度达到20%时,只有锌-0.2Li和锌-1.4Li合金无细胞毒性,其他合金细胞毒性轻微。当提取物浓度超过40%时,几乎所有的合金都表现出细胞毒性,细胞生存能力随提取物浓度而逐渐降低。相比之下,ZnLi合金提取物中L-929细胞的活性低于锌提取物,但锌和ZnLi合金之间的细胞活性差异随着提取物浓度和凝固日的升高而降低。在ZnLi合金中,提取浓度在60%以内的Zn-0.2Li和Zn-1.4Li合金表现出更高的细胞活力,表明前两种合金具有更好的细胞相容性。值得一提的是,高浓度提取物的高毒性是常见现象。
如图12b所示,锌和ZnLi合金提取物的pH值比对照组高约0.4,pH值随着Li含量的增加而增加。提取物中的Zn2+浓度随着Li含量的总体趋势而下降,从纯锌的30.84μg/L降至Zn-1.4Li合金的24μg/L。Zn-0.5Li合金的较高的Zn2+浓度与SBF中的离子释放相似,这可能是由Zn-0.5Li合金的不均匀腐蚀引起的。同时,Li+浓度随着Li含量的增加而增加,从Zn-0.2Li合金的0.16μg/L到Zn-1.4Li合金的0.85μg/L,表现出Li对ZnLi合金细胞毒性的作用越来越大。
Aiming to determine the role of Li in cytotoxicity of ZnLi alloys, the L-929 cells viabilities of Zn and Zn-(0.2–1.4)Li alloys after being cultivated in different concentration extracts for 1 day is shown in Fig. 12. According to ISO10993-5: 1999 standard, Zn promotes cell proliferation with cell viabilities over 100% when its extract concentrations are within 40%. However, it shows cytotoxicity with cell viabilities under 75% when its extract concentrations are beyond 60%. For ZneLi alloys, 10% extracts of Zn-(0.2–1.4)Li alloys show no cytotoxicity, and those of Zn-0.2Li and Zn-1.4Li alloys promote cell proliferation. When extract concentration reaches 20%, only Zn-0.2Li and Zn-1.4Li alloys exhibit no cytotoxicity while the other alloys show slight cytotoxicity. When extract concentration is over 40%, almost all the alloys exhibit cytotoxicity, and the cell viabilities decrease continuously with extract concentration. Comparatively, the viabilities of L-929 cells in the ZneLi alloy extracts are lower than that in the Zn extracts, but the discrepancy between cell viabilities between Zn and the ZnLi alloys decrease with rising extract concentration and culturing days. Among the ZnLi alloys, Zn-0.2Li and Zn-1.4Li alloys with extract concentrations within 60% show higher cell viabilities than those of the other alloys in general, indicating better cytocompatibility of the former two alloys. It is worthy to mention that high toxicity of high concentration extracts is a common phenomenon for variety materials.
As exhibited in Fig. 12b, pH values of Zn and ZneLi alloys extracts are about 0.4 higher than that of the control group, and the pH values increase with increasing Li content. Zn2+ concentration in the extracts decreases with Li content in a general trend, from 30.84 μg/L for pure Zn down to 24 μg/L for Zn-1.4Li alloy. The higher Zn2+ concentration for Zn-0.5Li alloy is similar to the ion release in SBF (Fig. 7a), which may be caused by the nonuniform corrosion in Zn-0.5Li alloy. Meanwhile, Li+ concentration increases with Li content, from 0.16 μg/L for Zn-0.2Li alloy up to 0.85 μg/L for Zn-1.4Li alloy, exhibiting the increasingly role of Li on the cytotoxicity of the ZneLi alloys.