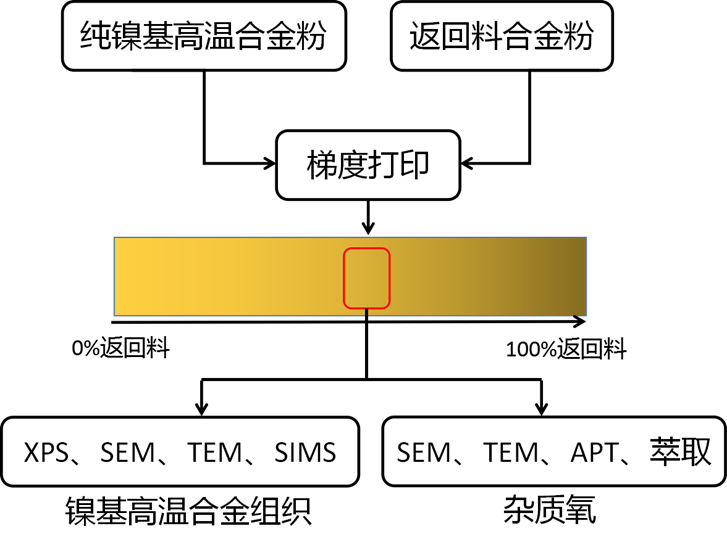
发明了研究氧含量对镍基高温合金组织性能的研究方法,属于镍基高温合金技术领域。包括以下步骤:S1、将高氧镍基返回料合金粉末放入送料桶的第一通道中,低氧镍基合金粉末放入送料桶的第二通道中;S2、启动第一通道的第一送料盘和第二通道的第二送料盘,进行连续出料,得到逐层堆叠的混合打印粉末;S3、同时启动打印设备,逐层打印,得到氧含量梯度变化的镍基高温合金试样;其中,混合打印粉末中随着层数的增加,高氧镍基返回料合金粉末的质量百分数由0%-100%逐渐递增,低氧镍基合金粉末的质量百分数由100%-0%逐渐递减。本发明方法制备出的氧含量呈连续变化的梯度材料,能够为高通量快速表征氧含量对镍基高温合金组织性能影响提供原型材料。
A research method for studying the effect of oxygen content on the microstructure properties of nickel-based superalloys was invented, which belongs to the technical field of nickel-based superalloys. Including the following steps: S1, put the high oxygen nickel base return material alloy powder into the first channel of the feeding barrel, low oxygen nickel base alloy powder into the second channel of the feeding barrel; S2. Start the first feeding tray of the first channel and the second feeding tray of the second channel to carry out continuous discharge and obtain the mixed printing powder stacked layer by layer; S3. At the same time, start the printing equipment, print layer by layer, and obtain the nickel-based superalloy sample with the change of oxygen content gradient; Among them, with the increase of the number of layers in the mixed printing powder, the mass percentage of the high oxygen nickel base return material alloy powder gradually increases from 0% to 100%, and the mass percentage of low oxygen nickel base alloy powder gradually decreases from 100% to 0%. The gradient material with continuously changing oxygen content prepared by the method of the invention can provide a prototype material for rapid characterization of the effect of oxygen content on the microstructure properties of nickel-based superalloys with high flux.